Naming and brief history of Chandpur district
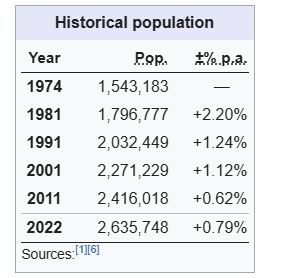
The name of the dense green land of 1704.06 sq km. spread across the banks of the Meghna, Dakatia, Dhanagoda rivers is Chandpur. 26,00,263 people live in this land amidst utmost care and affection. The moon in the sky shines on this green land. It covers a prosperous township of a thousand years of developed civilization. The source of soft light is the moon, the locality, Niketan or village township is Pur. The township built with the combination of these two is Chandpur. Let’s look back at the history and tradition of Chandpur.
Naming of Chandpur: 1779 AD. During the British rule, the map of the then Bengal drawn by the English surveyor Major James Rennell had an unknown township named Chandpur. At that time, the office and court of Chandpur was located in a place called Narsinghpur (which has now disappeared into the riverbed) to the south of Chandpur. The confluence of the Padma and Meghna was about 60 miles southwest of the present place. This area has now disappeared due to the erosion of the Meghna River. During the reign of the Bar Bhuiyans, the Chandpur region was under the control of Chandra Ray, the landlord of Bikrampur. He established an administrative center in this region. According to historian J. M. Sengupta, the name of this region is Chandpur after Chandra Ray.
According to another opinion, the name of this region is Chandpur after the name of Chand Fakir of Purindpur Mahalla of Chandpur city (Koralia). According to some, an administrator named Shah Ahmed Chand came from Delhi in the 15th century and established a river port here. Chandpur was named after him. He lived in the Purindpur area. The Firoz Shahi Mosque of Hajiganj is one of the most important examples of Muslim architecture. It is known from the inscription that it was built by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah’s Dewan Firoz Khan Lashkar. The administrative headquarters of the famous Mughal ruler Abdullah was in the village of Alipur under Hajiganj Upazila. Here is the famous Alamgiri five-domed mosque named after King Alamgir, the three-domed mosque built by Shahazada Shuja and the tombs of the brave generals of the Mughal period, which are currently known as the tombs of the Alids. As a result of the administrative reorganization during the British period, the first Chandpur subdivision was created in 1878. On 1 October 1896, Chandpur city was declared a municipality. On 15 February 1984, Chandpur emerged as a district.
The present Chandpur was included in the Samatata kingdom in ancient Bengal. The Chinese traveler Wan Chuang arrived in the Samatata kingdom towards the end of the second half of the 7th century AD, as per his travelogue. He described Samatata as a low-lying wetland on the seashore, which is what this region is all about. There is evidence that the kings of the Gupta Pala and Sena dynasties of ancient Bengal ruled this region. However, no distinct original name for the area has been identified.
After the conquest of Bengal by Ikhtiyar-ud-din Mohammad-bin-Bakhtiyar Khilji, the entire Bengal came under Muslim rule, and this region naturally came under Muslim rule. There is evidence in history that Sultan Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah ruled this region in particular.
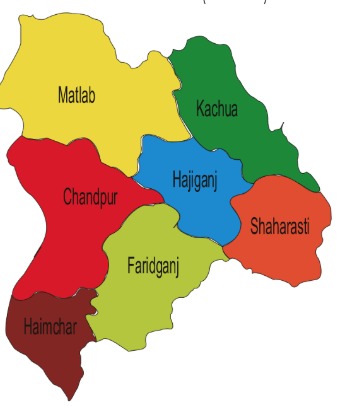
According to J. F. Brainy C. S., King Todarmal introduced 19 divisions for the Mughal administration in 1588 AD. One of these 19 divisions was the Sonargaon Sarkar, which included Tripura and Noakhali. Until 1722 AD, the original Sarkar of Todarmal and 1 of the 13 Chaklas or military jurisdictions annexed by Shah Shuja in 1658 was known as Dhaka or Jahangirnagar. Until 1960 AD, the district was called Tripura District. At that time, this district consisted of 4 subdivisions. They were: Sadar Uttar, Sadar Dakshin, Brahmanbaria and Chandpur. At that time, there were 21 thanas and 362 union councils. There were 5 thanas in Chandpur subdivision. They were: Chandpur, Faridganj, Hajiganj, Kachua and Matlab.

During the Great War of Independence, Chandpur began to be liberated from the enemy from 28 March to 7 April. On 7 April at 9 am, the Pakistani occupying forces first launched an air attack on Puran Bazar in Chandpur. There was a frontal battle between the Pakistani occupying forces and the freedom fighters in several places in Chandpur. Among them are Baburhat, Technical High School, Bakharpur Majumdar Bari, and a place called Gazipur Ottali in Faridganj. Chandpur was completely liberated from the enemy at 10 pm on 8 December 1971. In 1984, Chandpur was elevated from a subdivision to a district.